Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
The Covid-19 Antigen Rapid Test is a qualitative membrane based chromatographic immunoassay for the qualitative detection of the nucleocapsid protein antigen from Covid-19 in human nasal swab specimens.
When specimens are processed and added to the test cassette, Covid-19 antigens, if present in the specimen, will react with the anti-Covid-19 antibody-coated particles, which have been pre-coated on the test strip. The mixture then migrates upward on the membrane by capillary action. The antigen-conjugate complexes migrate across the test strip to the reaction area and are captured by a line of antibody bound on the membrane. Test results are interpreted visually at 15 minutes based on the presence or absence of visually colored lines.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
- The Covid-19 Antigen Rapid Test is for in vitro diagnostic use only. The test should be used for the detection of Covid-19 antigens in nasal swab specimens only. The intensity of the test line does not necessarily correlate to Covid-19 viral titer in the specimen.
- Specimens should be tested as quickly as possible after specimen collection and at most within the hour following collection.
- Use of viral transport media may result in decreased test sensitivity.
- A false-negative test may result if the level of antigen in a sample is below the detection limit of the test or if the sample was collected incorrectly.
- Test results should be correlated with other clinical data available to the physician.
- A positive test result does not rule out co-infections with other pathogens.
- A positive test result does not differentiate between SARS-CoV and Covid-19.
- A negative test result is not intended to rule out other viral or bacterial infections.
- A negative result, from a patient with symptom onset beyond seven days, should be treated as presumptive and confirmed with a molecular assay, if necessary, for clinical management.
- If the differentiation of specific SARS viruses and strains is needed, additional testing is required.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
- Possible discomfort during sample collection.
- Possible incorrect test results (see Result Interpretation section).
Potential benefits include:
- The results, along with other information, can help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your care.
- The results of this test may help limit the spread of COVID-19 to your family and others in your community.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Another type of test is an antibody test. A COVID-19 antibody test detects antibodies that have been produced by your immune system in response to a previous COVID-19 infection or vaccination. Antibody tests are not suitable for diagnosing an active COVID-19 infection.
For more information on the different kinds of COVID-19 tests, please visit: https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumerupdates/coronavirus-disease-2019-testing-basics.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.

A positive result means that it is very likely you have COVID-19 because proteins from the virus that causes COVID-19 were found in your sample. You should self-isolate from others and contact a healthcare provider for medical advice about your positive result. Your healthcare provider will work with you to determine how best to care for you based on your test result, medical history, and symptoms.
Click here to view more.

A negative test result indicates that antigens from the virus that causes COVID-19 were not found in your sample. If you have symptoms, you likely do not have COVID-19. However, negative results do not rule out SARS-CoV-2 infection. It is possible for this test to give a negative result that is incorrect (false negative) in some people with COVID-19. This means that you could possibly still have COVID-19 even though the test is negative. For example, you may get a false negative result if you did not perform the test correctly or if the level of antigen from the virus causing COVID-19 was below the test limits. The amount of antigen in a sample may decrease the longer you have symptoms of infection. If you test negative and continue to experience symptoms of fever, cough and/or shortness of breath you should seek follow up care with your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider will consider the test result together with all other aspects of your medical history (such as symptoms, possible exposures, and geographical location of places you have recently traveled) in deciding how to care for you. Your healthcare provider may suggest you need another test to determine if you have contracted the virus causing COVID-19. It is important that you work with your healthcare provider to help you understand the next steps you should take.
Click here to view more.
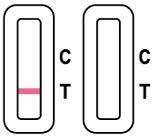
An invalid result means the test was not able to tell if you have COVID-19 or not. If the test is invalid, a new swab should be used to collect a new nasal specimen and the test should be run again, using a new test cassette and extraction buffer tube. If the problem persists, call (800) 838-9502 for assistance. Customer Service hours are 5a.m. – 5 p.m. (PST), 7 days a week.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
We also recommend you visit the CDC, the TSA, and your airline carrier websites, to view the latest documentation and accepted testing requirements for your destination.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
- Short Descriptor: SARSCOV CORONAVIRUS AG IA
- Medium Descriptor: IAAD IA SEVERE AQT RESPIR SYND CORONAVIRUS
- Long Descriptor: Infectious agent antigen detection by immunoassay technique, (eg, enzyme immunoassay
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
- Description : SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) Ag [Presence] in Upper respiratory specimen by Rapid immunoassay
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.
| Current Expiration Dates | New Expiration Dates |
|---|---|
| October 2022 | February 2023 |
| November 2022 | March 2023 |
| December 2022 | April 2023 |
| January 2023 | May 2023 |
| February 2023 | June 2023 |
| March 2023 | July 2023 |
Click here to view more.
Click here to view more.

